EDB Postgres Distributed for Kubernetes is now available in preview;
additional Q1 releases bring better performance, storage efficiency, and data consistency to Postgres
In today's dynamic, data-driven economy, downtime is not an option. The demand for continuous and global data availability has never been higher. In turn, data infrastructure must be highly available (nearly “always on”), resilient, and consistent — even in the face of extreme high throughput.
Enter EDB Postgres Distributed (PGD) for Kubernetes, a fully commercially supported operator that enables game-changing high availability for cloud-native PostgreSQL deployments — now available in preview.
At the core of the new Kubernetes solution is PGD, EDB’s high availability deployment for “always on” Postgres, offering up to 99.999% uptime guaranteed, and up to 5X improved data replication performance versus native Postgres logical replication. PGD uses an active/active architecture, conflict resolution via Raft-based consensus, and data loss protection to help ensure business continuity and protect against unplanned outages.
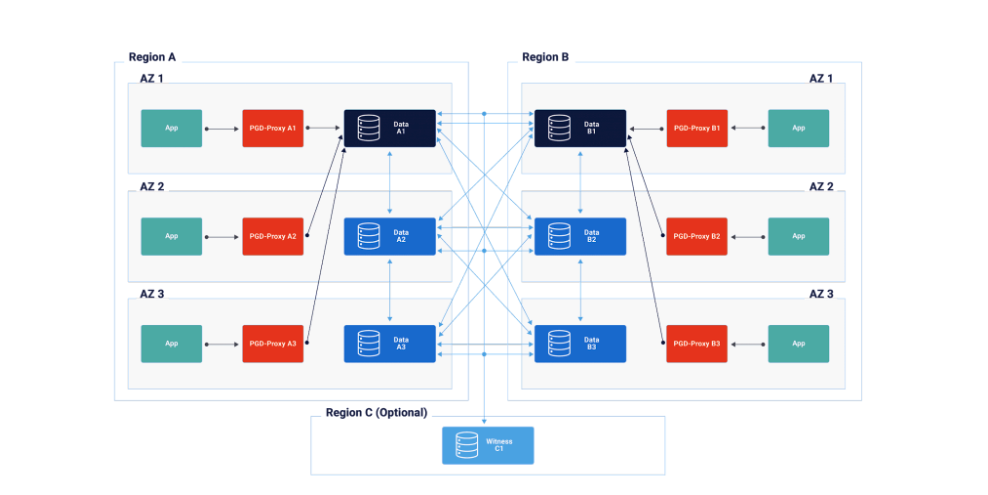
Now, with EDB’s PGD for Kubernetes operator, PGD’s extreme HA and geo-distributed capabilities can be easily deployed across your cloud-native Kubernetes environments. PGD for Kubernetes brings additional benefits, including:
Seamless Kubernetes API Integration:
Use the Kubernetes API to seamlessly manage distributed Postgres high availability deployments. With the EDB Postgres Distributed operator pattern, managing complex setups becomes a breeze, offering finesse and flexibility to administrators.
Declarative Configuration:
Say goodbye to manual database management tasks for Kubernetes environments. PGD enables declarative configuration, allowing you to deploy, scale, and maintain databases with automation that streamlines operational workflows, further reducing administrative burdens.
Advanced Observability:
Gain critical insights into performance, capacity, and potential faults that could impact operations of your Postgres deployments with integrated monitoring and logging. Enhanced diagnostics empower strategic decision-making, helping ensure optimal performance and uptime.
Secure by Default:
Security can be challenging in complex cloud-native and distributed environments. PGD for Kubernetes prioritizes security at all layers, from source code to Kubernetes clusters, providing robust security protocols and mission-critical features — such as geo-fencing and role-based access control — to help safeguard your data.
Key Features That Empower Your EDB Postgres Distributed for Kubernetes Deployments:
- Automated Deployment and Scaling: Kubernetes-native management tooling simplifies administrative tasks.
- Geo-distributed, active-active architectures: Enhance application performance and meet data sovereignty, localization, and residency requirements.
- Disaster Recovery Made Easy: Leverage multi-region, continuous availability architectures for seamless disaster recovery.
- Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) for PostgreSQL: Tailor database features to suit your specific application and workload requirements.
- Smooth Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: Seamlessly integrate database management with DevOps and infrastructure platform processes.
- Declarative Management: Specify database requirements and let PGD handle the rest.
- Advanced Durability Operations: Effortlessly adjust resources to accommodate fluctuating workloads.
- Monitoring and Logging Integration: Maintain visibility into database performance metrics.
- Community and EDB Support: Benefit from full access to EDB's deep internal expertise, plus PostgreSQL community-driven support.
EDB, CloudNativePG, and Kubernetes:
EDB is not just a supporter of open source PostgreSQL; we're driving its evolution. With more than 300 Postgres specialists and our active contributions to the PostgreSQL community, we're at the forefront of PostgreSQL.
As part of our commitment to the Postgres and Kubernetes communities, two years ago we released a free and open source Kubernetes operator, CloudNativePG.
CloudNativePG recently hit a milestone of adoption and now has 3,000+ stargazers on GitHub! You can read more about how CloudNativePG is simplifying complex database problems by leaning into Kubernetes’ dynamic scaling and self-healing capabilities in this blog from EDB’s VP of Cloud Native, Gabriele Bartolini.
Recent EDB Features:
In addition to the PGD for Kubernetes preview, throughout Q1 EDB released a range of improvements to our Postgres solutions that bring more performance, storage efficiency, and data consistency to a wide range of deployments — on prem, private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid.
- Postgres workload reports: Performance diagnostics in the familiar format of Oracle AWR reports that advance database performance analysis and improve diagnosis and troubleshooting. Read more: Elevating Diagnostics and Troubleshooting With EDB Postgres Workload Reports
- Apply_delay command for PGD: apply_delay enables the creation of a delayed read-only replica, providing additional options for disaster recovery and mitigating the impact of human error, such as accidental DROP table statements
- PostgreSQL extension pg_squeeze support: Supporting pg_squeeze on our database distributions and across different deployment types reduces bloat and improves query performance. Read more: Release Radar: Reducing Bloat and Improving Query Performance With EDB Support for pg_squeeze
- PostgreSQL extension Bluefin support: Bluefin is designed to provide data compaction and delta compression, which makes it particularly useful for storing time-series data, common in IoT and monitoring use cases.
- Updated EDB .NET connector publishing on NuGet: Saves customers time in deployment and maintenance, as dependency management is delegated to NuGet, providing automatic .NET SDK version matching. Read more: Improving Developer Experience: Updated EDB .NET Connector Now Published on NuGet.
Stop by our booth at KubeCon to learn more:
Come visit us at BOOTH G30 and see all the innovation EDB is bringing to PostgreSQL, CloudNativePG, and Kubernetes.
