PostgreSQL for Public Sector Organizations
Take the first step towards a more flexible, cost-efficient, and scalable database management solution
An introduction to PostgreSQL for the public sector
PostgreSQL, or Postgres, is an open-source relational database management system known for its robustness, flexibility, and scalability. Due to its built-in security, ability to scale, and cost-effectiveness, it is an ideal choice for various public sector organizations, including:
- Government and civilian agencies: Manage confidential data, personal information and more.
- Law enforcement agencies: Ensure secure evidence storage and compliant case management.
- Educational institutions: Store student records, academic content, and research data.
- Public healthcare providers: Securely handle patient information, medical records, and healthcare analytics.
Benefits of Using PostgreSQL
- Cost-effectiveness: Open-source with no licensing fees, perfect for budget-conscious public sector entities.
- Scalability and performance: Handles large data volumes and high user loads effortlessly.
- Security: Built-in features ensure the protection of sensitive information.
- Flexibility: Supports various data types and extensions to meet diverse needs.
- Community and support: Backed by a vibrant community offering continuous improvements and support.
- Compliance: Designed to help meet regulatory requirements and standards.
EnterpriseDB (EDB) provides enterprise-class PostgreSQL products and services tailored for public sector needs. EDB enhances PostgreSQL with advanced security, performance optimization, and comprehensive support, ensuring that your organization leverages the full potential of PostgreSQL while maintaining data integrity and security.
Explore how to strengthen and extend PostgreSQL.
Explore some common government agency database challenges
From ensuring data security and compliance to managing scalability and performance, public sector organizations often encounter unique challenges in database management.
| Data Security and Compliance | Public sector organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive information, from personal citizen data to classified government records. Ensuring the security of this data and compliance with regulatory standards is a significant challenge. |
| Scalability and Performance | As public sector organizations grow, their data needs expand. Databases must scale to accommodate increasing volumes of data and user load, and performance issues can hinder the efficiency of public services. |
| Budget Constraints and Cost-Effectiveness | Operating within tight budget constraints is a common reality for public sector entities. Expensive proprietary database solutions can strain financial resources. |
| Integration with Legacy Systems | Many public sector organizations rely on legacy systems that are integral to their operations. Integrating new database solutions with these older systems can be complex and costly. |
PostgreSQL enables public sector organizations to enhance their data management capabilities, improve operational efficiency, and deliver better services to their constituents.
Lock Down Data with Confidence
PostgreSQL boasts a rock-solid security architecture, making it the go-to choice for organizations with stringent compliance requirements. Out-of-the-box features provide unparalleled control over sensitive data and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
PostgreSQL offerings for security:
- Robust authentication: Easily set up secure user authentication, including password encryption, multi-factor authentication, and integration.
- Granular access control: Define user roles and permissions with pinpoint accuracy, ensuring users only access the data they absolutely need.
- Encryption at rest and in transit: Use advanced encryption options to safeguard data at rest within the database and in transit between your application and the server.
EnterpriseDB extends PostgreSQL’s security features even further.
Beyond the basics: Adopting a Zero Trust model for security
The term Zero Trust refers to a security model that assumes that no user or device can be fully trusted, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network perimeter. As a result, it requires continuous verification of every user’s identity, device, and access privileges before granting them access to resources.
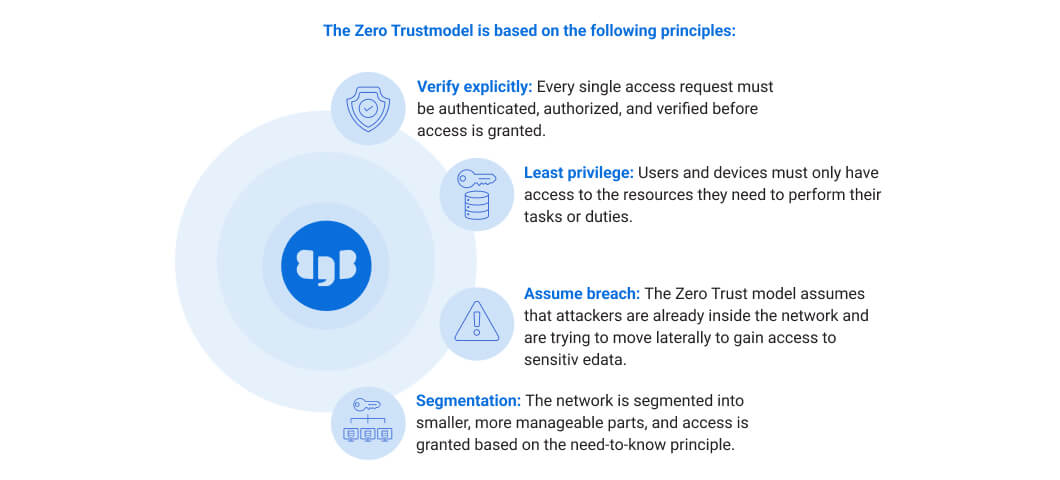
EDB Postgres provides a foundational platform for secure and auditable data storage, with a flexible API that can be integrated with many other Zero Trust security components.
Learn how you can accelerate your Zero Trust journey with EDB Postgres.
Maintaining an Always-On Database
Ensuring high availability and robust disaster recovery is critical for public sector organizations. Sometimes even high availability (traditionally maxing out at 99.99% uptime) is simply not high enough.
Highly available databases that go above and beyond are essential to public sector organizations that depend on mission-critical, 24/7 access to data.
Why high availability is important
For government agencies and other public organizations, high availability is not just a convenience—it's a necessity. Downtime can disrupt critical services, delay important processes, and erode public trust.
High availability ensures that systems remain operational, enabling continuous access to vital information and uninterrupted service delivery.
Distributed PostgreSQL solution for disaster recovery
Disaster recovery involves strategies and systems to quickly restore data access and functionality after catastrophic events such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or major system failures.
With up to 99.999% uptime and 5X throughput performance vs. native logical replication, EDB Postgres Distributed helps public sector organizations:
- Avoid downtime risks
- Optimize Always-On architectures for seamless upgrades
- Comply with data localization laws
- Ensure PostgreSQL cross-version compatibility
Learn more about achieving Extreme High Availability with EDB Postgres Distributed.
Optimizing for peak performance
Government agency databases must be optimized for peak performance to provide efficient and responsive services. Effective performance optimization and tuning are essential for handling large volumes of data and high user loads.
To achieve optimal database performance, public sector organizations should focus on several key areas:
| Indexing and Query Optimization | Proper indexing and efficient query design are crucial for fast data retrieval and minimizing resource consumption. |
| Configuration Tuning | Adjusting database configuration settings to match the specific workload and hardware environment can significantly enhance performance. |
| Resource Management | Effective allocation and management of CPU, memory, and storage resources ensure that the database operates smoothly under varying loads. |
| Monitoring and Diagnostics | Continuous monitoring and diagnostics help identify performance bottlenecks and areas for improvement. |
Peak performance is a continuous journey
EDB offers a comprehensive suite of solutions to keep your PostgreSQL environment optimized:
Support and maintenance: Monitor, analyze, and tune your database performance with EDB Postgres Enterprise Manager
Professional services and support: Get bespoke support for performance tuning, guidance on configuration optimization, and proactive issue identification.
Training and certification: Invest in your team's expertise with our free and extensive training programs and certifications, empowering them to optimize PostgreSQL for your specific needs.
Partner with EDB to unlock the full potential of PostgreSQL and achieve unparalleled performance.
Adapt quickly and efficiently to your agency’s evolving needs
Public sector agencies often manage growing amounts of data and increasingly complex workloads. Ensuring that database systems can scale effectively and remain flexible is essential for meeting these demands and delivering efficient, responsive services to the public.
Ensuring databases can handle this growth requires careful planning and the right tools:
- Seamless scaling: PostgreSQL enables effortless scaling for government agency databases. Add resources on-demand, accommodating growth without compromising performance.
- Flexible deployment: Deploy PostgreSQL on-premises, in the cloud or in a hybrid environment. Enjoy the flexibility to adapt your deployment model as your needs evolve.
- Open-source advantage: The open-source nature of PostgreSQL empowers you to customize the database to meet your specific requirements, ensuring a perfect fit for your unique workflows.
EDB extends the core Postgres offering, providing additional tools and expertise to streamline your scaling journey and ensure a future-proof database solution.
Learn how EDB can help your specific use case in the public sector.
Overcoming the limitations of other database management solutions
Not all database management solutions are equal. Some systems, such as Oracle have many drawbacks including:
- Vendor ecosystem lock-in: Businesses might face predatory contracts during renewal and high switching costs when trying to leave. It would also be harder to decouple from Oracle solutions the longer you stay invested, putting your applications and business at risk.
- Compoundingly high costs: To keep your business technologically competitive and reliable on Oracle, you may be compelled to pay for expensive services like support and maintenance. Pricing lists and tiers can also be confusing – leading to runaway costs.
- Rigid licenses and plans: Lack of flexibility, clarity, and accountability around vendor licenses and plans will limit the agility and longevity of digital transformation initiatives for business growth.
- Lack of forward interoperability: Integrating legacy vendor databases like Oracle with new technologies or data will require complex workarounds or code rewrites, challenging even for the most experienced developers.
Why public sector organizations are migrating to PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is rapidly becoming the preferred choice for public sector organizations looking to migrate from Oracle. Here’s why:
| Ecosystem diversity | Due to its open source licensing, users and businesses can do whatever they want with PostgreSQL, spawning a multitude of unique feature-rich solutions and projects in the community. Users can more easily find support, plug-ins, and integrations they need to achieve their objectives. |
| Diverse data type support | PostgreSQL supports all SQL data types, along with a range of non-SQL data like JSON, time series, numeric, geometric, boolean, images, and even network addresses. Users can even define their own complex data types, giving them the flexibility to build and align data to how they want it represented in applications. |
| Reliable uptime, without high costs | PostgreSQL offers all the High Availability and Backup features that users need – such as replication, point-in-time recovery, disaster recovery, and backup – already built into the solution. This ensures true five 9s of high availability and recovery, without the need for pricey Oracle HA and backup services. |
| Robust extensibility and integration | The catalog-driven nature of PostgreSQL doesn’t just allow a broader variety of information to be written into catalog tables, but that information can be written by users without needing to touch code. This allows users to more seamlessly extend the database to build new functions or integrate new data. |
| Elevated data security and access | The built-in security capabilities of PostgreSQL are extensive, covering authentication, access control, and privilege management systems, along with a variety of other functions that govern remote access permissions and data access. |
| Flexible and agile cloud deployments | Deploying or migrating PostgreSQL to cloud will require as much expertise as any database migration, but it’s easier to find a broad range of provider solutions for PostgreSQL, due to how flexible and scalable the solution is. |
The migration from Oracle to Postgres can be complex, but with the right tools and strategies, it can be done safely and securely.
Get detailed information on the best tools and practices for migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL.
Explore real-world success stories of public sector organizations
FBI protects high stakes, highly sensitive data with EDB Oracle Compatibility
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the primary law enforcement agency in the United States and a major part of our nation’s security and intelligence infrastructure. Agents investigate a wide range of serious threats, including terrorism, cyber attacks, and organized crime, and as part of their work, they must collect, analyze, and protect high-stakes, highly sensitive data.
Learn how EDB’s Postgres Advanced Server helps FBI leadership protect some of the government’s most sensitive data.
Indiana State University Modernizes Their Tuition Benefits and Tracking System with Postgres and EDB Support
Following a successful migration of its tuition benefits and tracking system—allowing them to provide and manage financial aid and veteran tuition assistance, Indiana State University knew they would need help maintaining their new database. Without that help, they would not be able to guarantee consistent performance and database availability, making it harder to access the systems they had just migrated.
Find out how EDB Support provided 24/7 access to Postgres experts to ensure an “Always-On” database for Indiana State University.
U.S. Army benefits from EDB’s robust PostgreSQL functionality
The United States Army has worked with EDB for more than 10 years, relying on their decades of PostgreSQL experience to support a wide range of mission critical projects and functions, including modeling and simulation, satellite communications, research initiatives, biometric identification, tactical deployments, and lifecycle management.
See why the U.S. Army has partnered with EDB for over 10 years.
Explore additional resources to learn more about PostgreSQL for the public sector
Postgres Five 9s ‘Always On’ Availability in the Public Sector
Accelerate Government’s Zero Trust Journey with EDB Postgres
7 Critical Success Factors for Moving to Open Source Databases (like Postgres)
5 Reasons Why Postgres is the Most Widely Adopted Open Source Database in Government
Accelerating Public Sector Software Modernization with Postgres Support
How Public Sector Orgs Can Achieve Postgres Extreme High Availability
PostgreSQL offers robust security, cost-efficiency, high performance, scalability, and compliance with government regulations, making it ideal for public sector applications.
EnterpriseDB provides security features such as data encryption, access controls, and regular security updates, as well as the following enhanced security measures:
- Zero Trust Framework “Ready”
- Role Based Access Control
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
- Column & Row Level Encryption
- Advanced Audit Logging
- DoD Iron Bank Approved
- SQL Injection Protection
- Password Policy Enforcement
- Advanced Data Redaction
- CIS Security Benchmarks
This ensures compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, alongside the following compliance standards for the public sector:
- Validated National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2
- Approved Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) Security Technical Information Guide (STIG)
- Section 508 Compliant with active Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT)
- Multiple Authority to Operate (ATOs) granted for Defense and Intelligence Classified Networks
Migrating from a legacy system to PostgreSQL involves several carefully planned steps to ensure a smooth and secure transition. Get more information on the steps, tools, and processes you’ll need for a successful migration: Oracle Migration Steps and Challenges
Because of its high security, operational flexibility, and easy scalability, PostgreSQL is used by agencies worldwide.
In the United States, agencies such as the U.S. Navy, the FBI, Wharton Research Data Services, and Indiana State University use PostgreSQL.
Outside the United States, public sector agencies such as the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Tourism use PostgreSQL.
PostgreSQL is released under the OSI-approved PostgreSQL Licence. There is no fee, even for use in commercial software products.
PostgreSQL is not FIPS compliant by default. However, the EnterpriseDB Cryptographic Module, deployed in the EDB Postgres Advanced Server database, has been awarded the FIPS 140-2 certification by the Cryptographic Module Validation Program (CMVP), operated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). This certification means the encryption in EDB Postgres is in full compliance with the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 standard after being tested to meet the benchmark by a laboratory authorized by the government to make such determinations. While the EnterpriseDB Cryptographic Module will provide FIPS 140-2 validated encryption in the distribution of EDB Postgres for Microsoft Windows, Red Hat Enterprise Linux installations will rely upon the RHEL OpenSSL FIPS compliant module.
To protect data in PostgreSQL, consider implementing the following security measures:
- Regularly update PostgreSQL to ensure you have the latest security patches and fixes.
- Enforce strong password policies for database users. Encourage the use of complex passwords and avoid default or easily guessable passwords.
- Implement the principle of least privilege. Grant only necessary permissions to users and limit access to sensitive data and system resources.
- Configure firewalls to restrict access to PostgreSQL ports (typically 5432) to trusted IP addresses and networks.
- Enable encryption for data in transit (SSL/TLS) and at rest (storage-level encryption). Use SSL certificates for host authentication and consider encrypting specific columns containing sensitive data.
- Utilize secure authentication methods such as SCRAM or GSSAPI, and avoid using plaintext authentication methods like trust or password.
- Enable auditing and logging features in PostgreSQL to monitor and track user activity, database access, and potential security breaches.
- Implement a robust backup strategy to ensure data integrity and availability in case of security incidents or data loss.
- Review and configure PostgreSQL settings and parameters to adhere to security best practices, such as disabling unnecessary features and hardening the server configuration.
- Keep the underlying operating system and dependencies up to date to mitigate vulnerabilities that could affect PostgreSQL's security.
- Deploy monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems to detect suspicious activities and potential security threats in real-time.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security weaknesses in your PostgreSQL deployment.
By implementing these security best practices, you can significantly enhance the security posture of your PostgreSQL environment and protect your data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security threats. For more information, check out: https://www.enterprisedb.com/postgresql-best-practices-encryption-monitoring
While PostgreSQL is a powerful and versatile database system, it does have some disadvantages:
- Complex configuration: Initial setup and tuning can be complex, requiring a good understanding of the system.
- Learning curve: For users and administrators new to PostgreSQL, the learning curve can be steep due to its rich feature set.
- Limited built-in tools: Compared to some commercial databases, PostgreSQL has fewer built-in management and monitoring tools, though many third-party options are available.
- Migration complexity: Migrating from other database systems to PostgreSQL can be complex and may require significant effort to address compatibility issues.
Increase public trust with 99.999% uptime and faster services.
Achieve high availability, optimal performance and scalability in database management.
Talk to our expert today.